Google’s Bard has transformed into Gemini What’s Different?
Google has launched Gemini, a new AI platform that is an upgrade from its previous chatbot, Bard. Gemini is powered by Google’s latest and most advanced large language model (LLM), which can handle multiple types of data and tasks. Gemini can also reason better and avoid errors that other AI models often make.
Gemini comes in three versions: Pro 1.0, Ultra 1.0, and Nano 1.0, each with different capabilities and features. Gemini is integrated with Google products such as Search, Gmail, and Workspace, and it is available in more than 170 countries.
US customers can access Gemini Advanced, which includes Gemini Ultra 1.0, Google’s most powerful AI model, for $19.99 a month. They also get two terabytes of cloud storage and other perks. Gemini Advanced is part of the Google One AI Premium plan, which is Google’s response to OpenAI and its chatbot ChatGPT. Gemini and ChatGPT are competing for the attention and loyalty of AI users, who have more choices than ever.
Bard is no longer available, but Gemini is based on Bard’s technology and design. Users who used Bard will not notice much difference when they switch to Gemini, except for the improved performance and functionality. Gemini also keeps the previous conversations that users had with Bard.
Gemini also replaces the AI features that were previously called Duet AI in Google’s Workspace apps like Gmail and Docs. These features help users with various work-related tasks, such as writing emails, organizing spreadsheets, and more. They are now also called Gemini, and they work the same way as before.
Bard vs Gemini: Which is Better?
Gemini is an upgrade from Bard in many ways. It has a larger and more diverse dataset, which makes it more accurate and nuanced. It also has a more advanced and versatile model, which makes it more capable and reliable. Gemini Advanced, which uses the Ultra 1.0 model, can handle complex tasks like coding, reasoning, and creating better than Bard. It also has a longer and richer conversation memory than Bard. Gemini can also do more tasks that Bard could not, such as deep research or creative writing. Gemini can also connect to the real world through Google Search and other services, which makes it more relevant and up-to-date. Gemini is more natural and engaging than Bard, and it offers a more dynamic and informative experience.
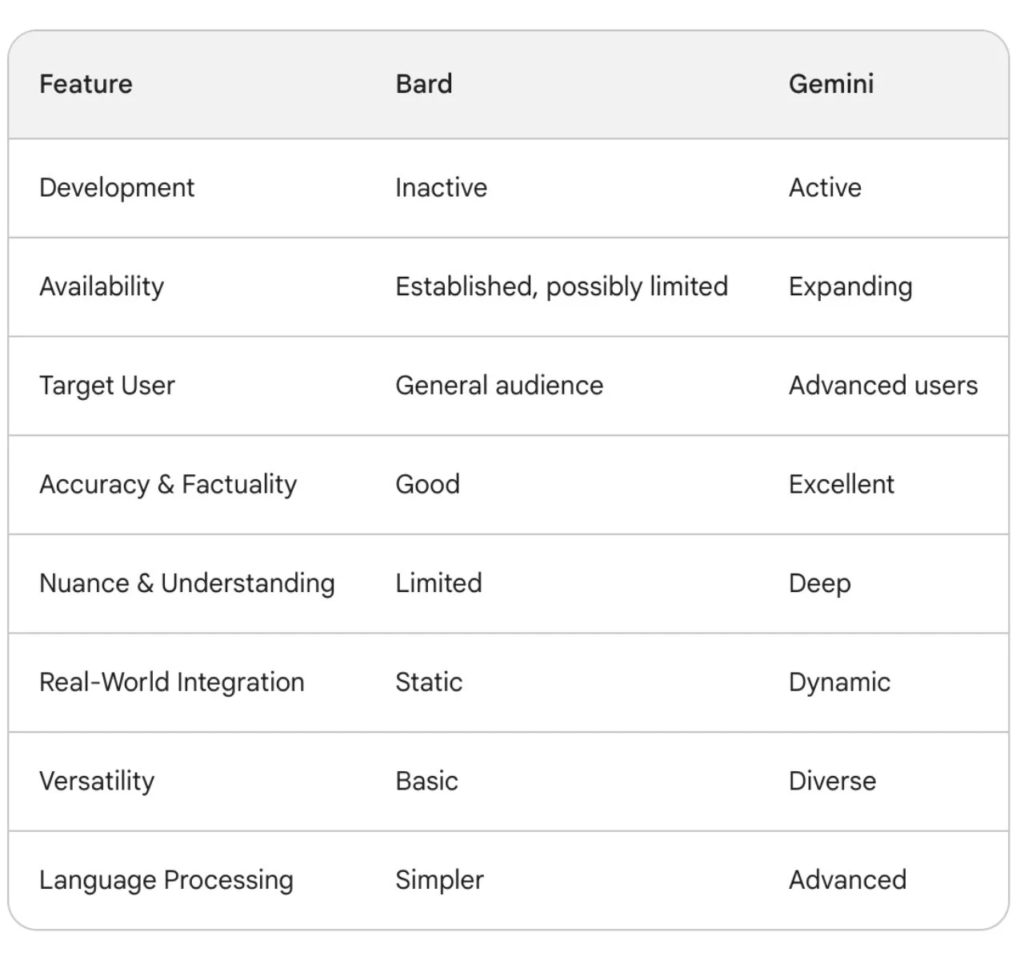
Key differences between Bard and Gemini
Underlying Architecture
Bard Primarily relied on Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), a traditional AI architecture that processes text sequentially, limiting its ability to grasp long-term dependencies and complex relationships between words.
Gemini, however, leverages transformers, a more advanced neural network architecture. Transformers can process entire sentences simultaneously, allowing for a deeper understanding of context, sentence structure, and word relationships. This enables Gemini to better capture humour, sarcasm, and emotional undertones.
Gemini also Possesses multimodal capabilities, meaning it can understand and process various information types like text, images, and audio. This allows Gemini to draw connections between different modalities, leading to richer and more comprehensive responses. Imagine asking about a historical event – Gemini could access and analyze both textual descriptions.
Data and Training
Gemini is trained on a much larger and more diverse dataset than Bard. This includes text, code, images, and audio, giving it a broader understanding of the world and language. Bard, however, is primarily focused on text-based data. Gemini also leverages specialized datasets for specific tasks, like high-quality images for visual content generation. Bard relied on more general text sources.
Like Bard, Gemini has access to real-time information through Google Search and other services, allowing it to stay up-to-date with current events and trends. Bard’s knowledge was static based on its training data.
Responses
As previously mentioned, Gemini has access to a larger and more diverse dataset than Bard. Pair this with improved processing algorithms, and a refined architecture, and you get responses that are generally more accurate and reliable.
Although Bard could offer informative answers, its factual accuracy wasn’t always optimal due to a smaller training dataset and less sophisticated architecture. While capable of generating grammatically correct sentences, Bard sometimes lacked the depth and nuance of human language, sometimes delivering responses that felt more machine-generated.
Language Processing
Gemini leverages more advanced neural network architectures like transformers, allowing for a deeper understanding of language context and relationships between words. Bard, however, used simpler recurrent neural networks, limiting its ability to grasp complex sentence structures and nuances.
Gemini can also process various information types like text, images, and audio, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the world and enabling richer responses. When it comes to text, it emphasizes understanding emotional and cultural contexts, leading to more natural and engaging responses. This ability allows it to capture humour, sarcasm, and emotional undertones in human language. Bard’s responses might have lacked these subtleties due to its less sophisticated architecture.
Real-World Integration
Gemini integrates with Google Search and other Google services, enabling it to access and process real-time information from the wider web. This allows it to stay up-to-date with current events, trends, and factual data, providing more relevant and contextually accurate responses compared to Bard.
Bard, on the other hand, on its static training data for information, and its answers were primarily based on its pre-trained knowledge, limiting its ability to adapt to new information or changing contexts.
Availability
Gemini is currently available in over 230 countries and territories, with ongoing efforts to expand further. However, it’s not yet universally accessible in all regions and is only limited to English. It seems geared towards users seeking advanced language modelling capabilities. Bard is only available in countries where Gemini has not been rolled out yet.
Final Thoughts
Bard was Google’s first AI chatbot that used LaMDA as its underlying model. It was designed for conversational interactions and could generate text, translate languages, and answer questions. However, it had some limitations in terms of performance, multimodal capabilities, and integration with other Google products and services.
Gemini is the new AI platform that replaces Bard. It uses a more advanced and versatile model with the same name. It can process and generate text, images, audio, video, and code, and it can handle more complex tasks such as reasoning, problem-solving, and creating. It is also integrated with Google Search, Gmail, Workspace, and more. Gemini comes in three versions: Pro 1.0, Ultra 1.0, and Nano 1.0, each with different features and capabilities. Gemini Advanced, which includes Gemini Ultra 1.0, is available as part of a Google One AI Premium subscription plan.
Overall, Gemini is a major upgrade from Bard in terms of accuracy, nuance, and real-world integration. It offers a more dynamic and informative experience for users who want to collaborate with AI in various domains. However, Bard is not completely obsolete, as it still serves as the foundation and inspiration for Gemini. Both Bard and Gemini represent significant achievements in AI technology and innovation


